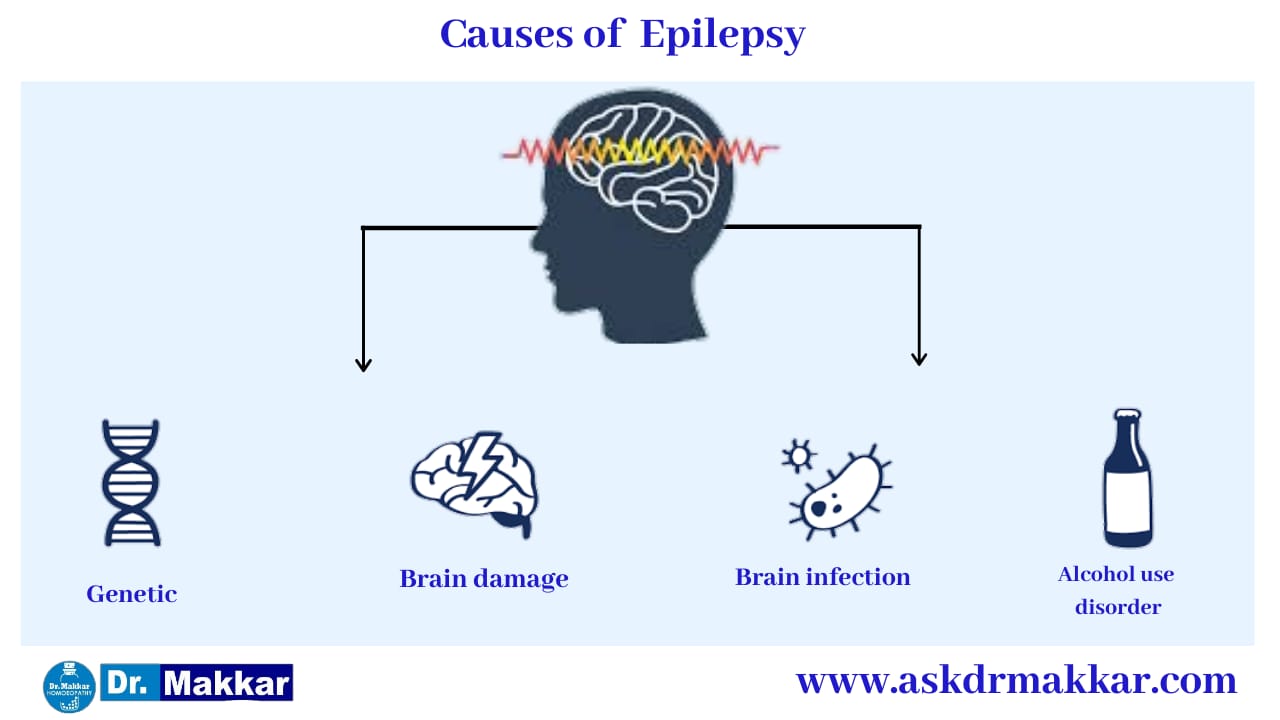
More often, causes will be idiopathic (unknown). Sometimes it may be symptomatic, i.e., having base for the suffering – suspected cause/disease. Commonly, seizure or twitching occurs when the brain/nerves lack essentials like oxygen, glucose, sodium, calcium, etc. Medical science has also identified innumerable causative factors for the occurrence of seizure disorders. The most common causes are:
Hereditary – Chromosomal abnormalities, autism, genetic predisposition, etc.
Attained during birth – Asphyxia developed as a complication of delivery, i.e., delay in conduction of delivery or due to cord around the neck or by ingestion of amniotic fluid, etc.
Physiological – Sleeplessness, overtime job, poor nutrition, poor growth, excess alcohol, sexual excesses, heat stroke , etc.
Psychological – Mental trauma /shock, fear, getting upset, anxiety, tension, depression, emotional conflicts, anger, loss, loneliness, etc.
Pathological – High fever, viral or bacterial infections (meningitis or encephalitis), ischaemia, high blood pressure, increased ventricular pressure, heart arrythmias, high sugar levels, metabolic disorders, vascular disorders/tumours, brain tumours, neurofibroma, parasite infections, etc.
Injury/trauma – Head injury from being hit while playing or due to surgical procedures to remove tumours or clots or druing forceps delivery, etc.
Drug induced – Seizures can also arise as a drug reaction during development (pregnancy period) or from drug dependency or from drug withdrawal which was held suddenly after having developed drug dependency (epilepsy or migraine), or from drugs poisoning with toxic doses, etc.
Generally in
Childhood – genetic predisposition, chromosomal abnormality, high fever, head injury , forceps delivery, asphyxia during delivery, bacterial or viral encephalitis, parasite infection, etc., come as common causes.
Adult – Alcohol, brain tumours, stroke, sleeplessness, metabolic disorders, head injury, meningitis, encephalitis, high fever, parasite infection, sclerosis, ageing atrophy, degenerative disorders, hypertension, diabetes , renal failure, etc., are common causes. More often, causes will be idiopathic (unknown). Sometimes it may be symptomatic, i.e., having base for the suffering – suspected cause/disease. Commonly, seizure or twitching occurs when the brain/nerves lack essentials like oxygen, glucose, sodium, calcium, etc. Medical science has also identified innumerable causative factors for the occurrence of seizure disorders. The most common causes are:
Hereditary – Chromosomal abnormalities, autism, genetic predisposition, etc.
Attained during birth – Asphyxia developed as a complication of delivery, i.e., delay in conduction of delivery or due to cord around the neck or by ingestion of amniotic fluid, etc.
Physiological – Sleeplessness, overtime job, poor nutrition, poor growth, excess alcohol, sexual excesses, heat stroke , etc.
Psychological – Mental trauma /shock, fear, getting upset, anxiety, tension, depression, emotional conflicts, anger, loss, loneliness, etc.
Pathological – High fever, viral or bacterial infections (meningitis or encephalitis), ischaemia, high blood pressure, increased ventricular pressure, heart arrythmias, high sugar levels, metabolic disorders, vascular disorders/tumours, brain tumours, neurofibroma, parasite infections, etc.
Injury/trauma – Head injury from being hit while playing or due to surgical procedures to remove tumours or clots or druing forceps delivery, etc.
Drug induced – Seizures can also arise as a drug reaction during development (pregnancy period) or from drug dependency or from drug withdrawal which was held suddenly after having developed drug dependency (epilepsy or migraine), or from drugs poisoning with toxic doses, etc.
Generally in
Childhood – genetic predisposition, chromosomal abnormality, high fever, head injury , forceps delivery, asphyxia during delivery, bacterial or viral encephalitis, parasite infection, etc., come as common causes.
Adult – Alcohol, brain tumours, stroke, sleeplessness, metabolic disorders, head injury, meningitis, encephalitis, high fever, parasite infection, sclerosis, ageing atrophy, degenerative disorders, hypertension, diabetes , renal failure, etc., are common causes.