Self-Checks/At-Home Testing
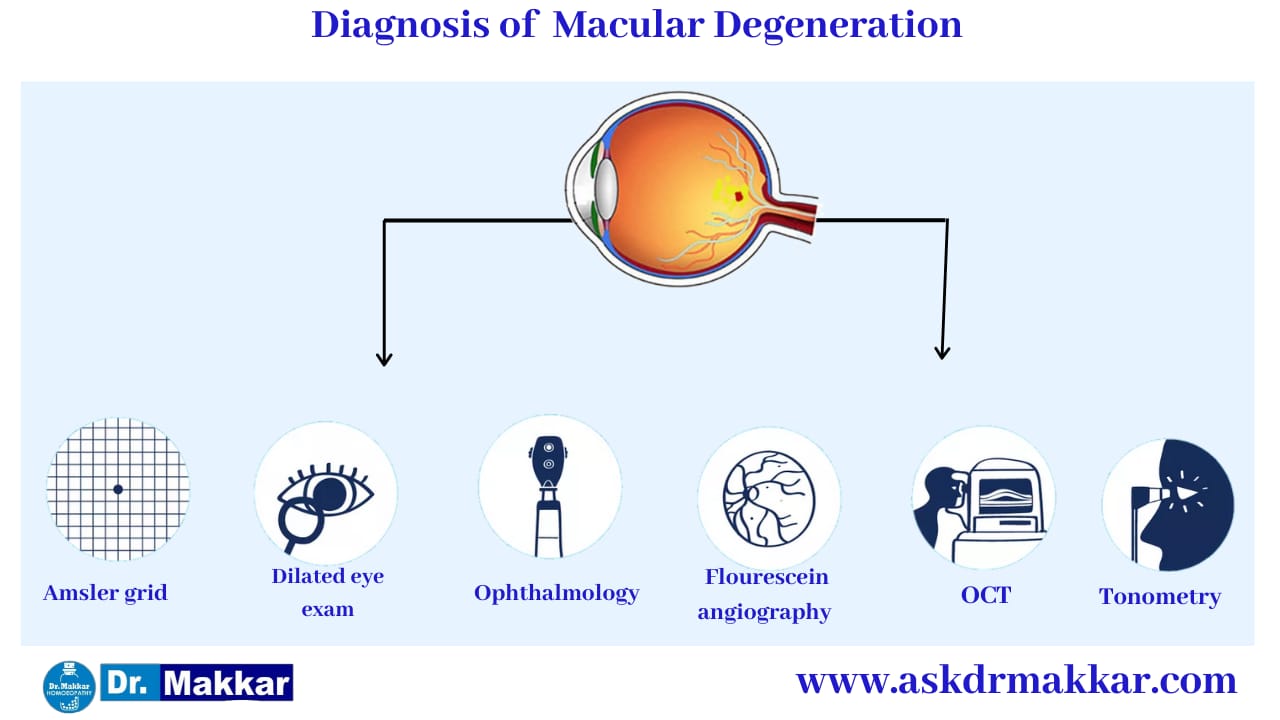
The Amsler grid (sometimes referred to as the Amsler chart) is perhaps the most common test that is used at home to screen for the possibility of wet AMD. The Amsler grid had been used since 1945.
The chart displays horizontal and vertical lines and is used to evaluate and monitor changes in a person's central visual field. The grid was developed by a Swiss ophthalmologist named Marc Amsler. The grid can be used to perform ongoing self-eye screenings at home.
Eye Examination and Tests
Macular degeneration can be discovered via symptoms that you notice at home, but also can be diagnosed during a scheduled yearly eye exam.
The initial part of wet AMD diagnostic testing is an eye examination, which takes place after the eyes are dilated. If macular degeneration is present, the ophthalmologist sees the presence of drusen (cellular debris present under the retina) as well as macular pigment changes. These changes can often be observed by the eye doctor before visual symptoms occur.
Screening Tools
Visual screening tools are often used for the initial evaluation of eye disorders such as AMD. The ophthalmologist uses an ophthalmoscope or a retinoscope a handheld instrument that checks refractive power using light emitted to the retina) to visually exam the eyes. There are many other tools and pieces of equipment that ophthalmologists commonly use to perform an eye exam.
Imaging
Imaging tests are commonly used to form a definitive diagnosis of AMD. There are two forms of AMD, the wet form and the dry form. Wet AMD involves new blood vessels that are not formed correctly. These dysfunctional blood vessels burst and cause bleeding in the eye.
This abnormal formation of blood vessels is also referred to as neovascularization. In wet AMD, neovascularization may be seen in or under the retina by means of imaging examinations.
Fundus Autofluorescence Imaging
Fundus autofluorescence (AF) imaging is a non-invasive test that utilizes the body’s natural fluorescence to examine the retina for signs of wet AMD. This test takes advantage of the body’s natural ability to light up when exposed to certain types of light. The structures that light up are called fluorophores.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography is a non-invasive imaging test (no injections required) that shows details of the retina and provides very useful diagnostic information about the telltale signs of wet AMD (such as new/abnormal blood vessels, hemorrhaging, drusen, and more).
Indocyanine Green Angiography
Indocyanine green angiography is a diagnostic procedure that utilizes green dye to illuminate the blood flow in the choroid. The choroid is a layer of blood vessels located between the white of the eye (called the sclera) and the retina.
The test can help with differential diagnoses, because it allows for specific evaluation and analysis of the choroidal circulation. The choroidal circulation is the area in which vascular dysregulation (abnormal blood vessels) occurs in wet AMD.