Primary and Secondary Varicocele
Primary varicocele happens when the configuration of the left internal spermatic vein and the renal vein forms a high-pressure blood column. This often happens in combination with malfunctioning valves in the veins of these patients. The configuration prevents blood from escaping from the scrotal veins back into the systemic circulation. As a result, the blood pools and causes the veins to swell, or dilate, resulting in varicocele formation.[i]
A secondary varicocele occurs when a mass in the scrotum impedes blood flow in the internal spermatic vein.
Either a primary
Secondary varicocele can be classified in any of the three varicocele grades of the condition:
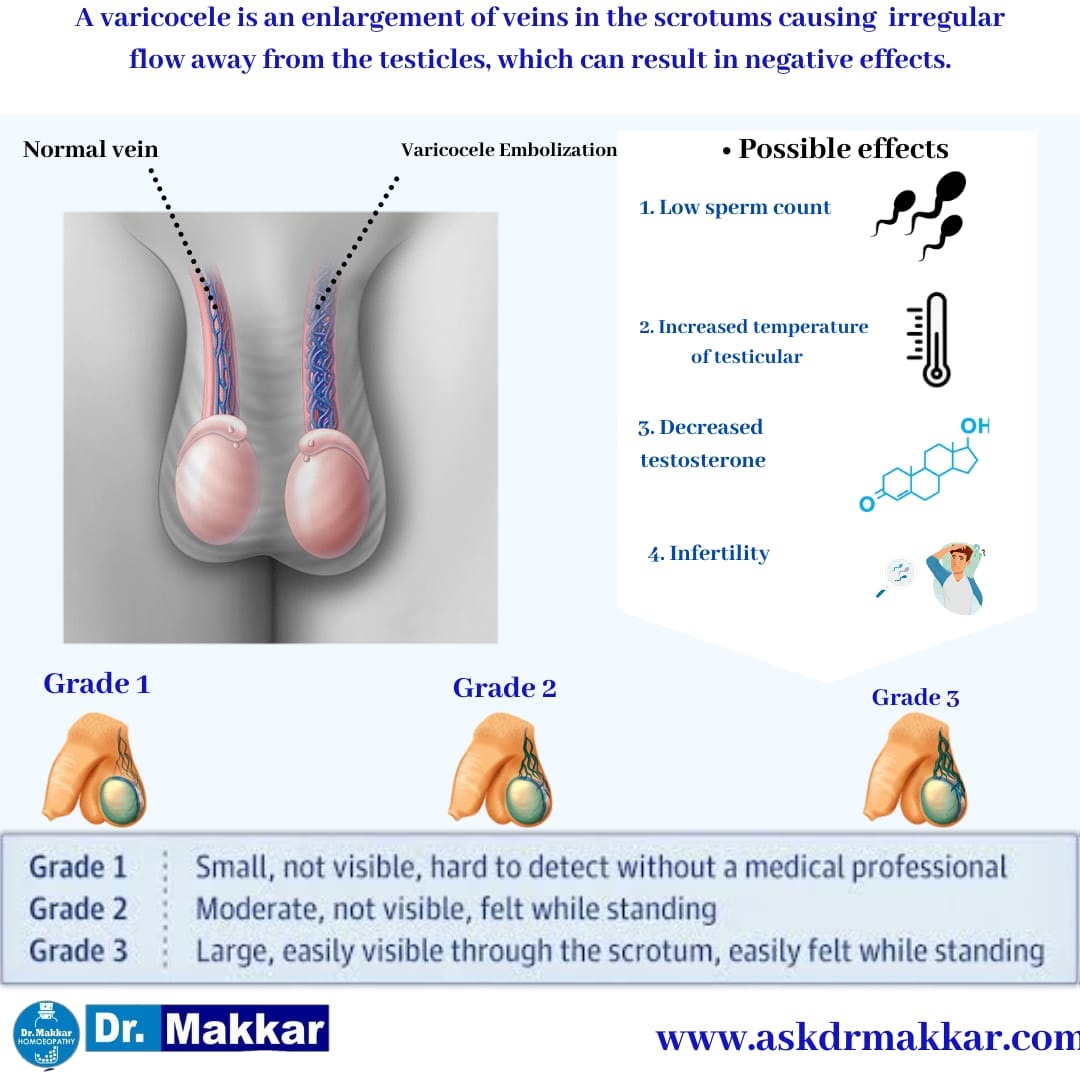
In this category, the dysfunctional veins are not visible. A doctor detects them during a physical exam while the patient performs a Valsalva maneuver. A Valsalva maneuver is a breathing exercise used as a diagnostic tool.
Grade II Classification of Varicocele
Varicoceles in this grade are still not visible, but can be felt during a doctor’s exam even without the aid of a Valsalva maneuver.
Grade III Classification of Varicocele
In this category, the varicoceles can be easily identified through the scrotum; there is no need to perform a physical exam to detect them.
Beyond the diagnosis classifications, there are two types of varicocele based on how the dysfunctional veins affect the body. The key difference between the classifications is how the varicocele affects the internal and external [medical term alert] iliac vein (one of three veins that drain the pelvic area of blood).
Pressure Varicoceles lead to retrograde blood pooling of the [medical term alert] internal spermatic vein (which carries deoxygenated blood from the testis), resulting in the varicocele. However, there is no varicocele to the internal or external iliac vein. This type of varicocele usually falls under the Grade I category.
Shunt Varicoceles have a severe pooling of blood that results in a large varicocele forming where damaged veins expand to the internal or external iliac vein. This type of varicocele is typically under the Grades II and III categories.